Federal Emergency Management Agency
 | |
 | |
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | April 1, 1979[1] |
| Jurisdiction | United States Department of Homeland Security |
| Headquarters | Washington, D.C., U.S. |
| Motto | Helping people before, during and after disasters[2] |
| Employees | 22,991 (Sep 2023)[3] |
| Annual budget | $29.5 billion (FY 2023)[4] |
| Agency executive |
|
| Parent department | U.S. Department of Homeland Security |
| Website | www |
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS), initially created under President Jimmy Carter by Presidential Reorganization Plan No. 3 of 1978 and implemented by two Executive Orders on April 1, 1979.[1] The agency's primary purpose is to coordinate the response to a disaster that has occurred in the United States and that overwhelms the resources of local and state authorities. The governor of the state in which the disaster occurs must declare a state of emergency and formally request from the President that FEMA and the federal government respond to the disaster. The only exception to the state's gubernatorial declaration requirement occurs when an emergency or disaster takes place on federal property or to a federal asset—for example, the 1995 bombing of the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, or the Space Shuttle Columbia in the 2003 return-flight disaster.
While on-the-ground support of disaster recovery efforts is a major part of FEMA's charter, the agency provides state and local governments with experts in specialized fields, funding for rebuilding efforts, and relief funds for infrastructure development by directing individuals to access low-interest loans, in conjunction with the Small Business Administration. In addition to this, FEMA provides funds for response personnel training throughout the United States and funds for non-federal entities to provide housing and services for migrants released from Department of Homeland Security custody.[5]
History
[edit]Federal emergency management in the U.S. has existed in one form or another for over 200 years.[6]
Prior to 1930s
[edit]A series of devastating fires struck the port city of Portsmouth, New Hampshire, early in the 19th century. The 7th U.S. Congress passed a measure in 1803 that provided relief for Portsmouth merchants by extending the time they had for remitting tariffs on imported goods. This is widely considered the first piece of legislation passed by the federal government that provided relief after a disaster.[7]
Between 1803 and 1930, ad hoc legislation was passed more than 100 times for relief or compensation after a disaster. Examples include the waiving of duties and tariffs to the merchants of New York City after the Great Fire of New York (1835). After the collapse of the John T. Ford's Theater in June 1893, the 54th Congress passed legislation compensating those who were injured in the building.[8]
Piecemeal approach (1930s–1960s)
[edit]After the start of the Great Depression in 1929, President Herbert Hoover had commissioned the Reconstruction Finance Corporation in 1932.[9] The purpose of the RFC was to lend money to banks and institutions to stimulate economic activity. RFC was also responsible for dispensing federal dollars in the wake of a disaster. RFC can be considered the first organized federal disaster response agency.
The Bureau of Public Roads in 1934 was given authority to finance the reconstruction of highways and roads after a disaster. The Flood Control Act of 1944 also gave the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers authority over flood control and irrigation projects and thus played a major role in disaster recovery from flooding.[10]
Department of Housing and Urban Development (1973–1979)
[edit]Federal disaster relief and recovery was brought under the umbrella of the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), in 1973 by Presidential Reorganization Plan No. 2 of 1973,[11] and the Federal Disaster Assistance Administration was created as an organizational unit within the department. This agency would oversee disasters until its incorporation into FEMA in 1978.[11]
Prior to implementation of Reorganization Plan No. 3 of 1978 by E.O. 12127 and E.O. 12148, many government agencies were still involved in disaster relief; in some cases, more than 100 separate agencies might be jockeying for control and jurisdiction of a disaster.[12]
Over the years, Congress increasingly extended the range of covered categories for assistance, and several presidential executive orders did the same. By enacting these various forms of legislative direction, Congress established a category for annual budgetary amounts of assistance to victims of various types of hazards or disasters, it specified the qualifications, and then it established or delegated the responsibilities to various federal and non-federal agencies.[13]
In time, this expanded array of agencies themselves underwent reorganization. One of the first such federal agencies was the Federal Civil Defense Administration, which operated within the Executive Office of the President. Functions to administer disaster relief were then given to the President himself, who delegated to the Housing and Home Finance Administration. Subsequently, a new office of the Office of Defense Mobilization was created. Then, the new Office of Defense and Civilian Mobilization, managed by the EOP; after that, the Office of Civil and Defense Mobilization, which renamed the former agency; then, the Office of Civil Defense, under the Department of Defense (DoD); the Department of Health, Education and Welfare (HEW); the Department of Agriculture; the Office of Emergency Planning (OEmP); the Defense Civil Preparedness Agency (replacing the OCD in the DoD); the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) and the General Services Administration (GSA) (upon termination of the OEmP).[13]
These actions demonstrated that, during those years, the nation's domestic preparedness was addressed by several disparate legislative actions, motivated by policy and budgetary earmarking, and not by a single, unifying, comprehensive strategy to meet the nation's needs over time.[14] Then, in 1978 an effort was made to consolidate the several singular functions; FEMA was created to house civil defense and disaster preparedness under one roof. This was a very controversial decision.[13]
FEMA as an independent agency (1979–2003)
[edit]

FEMA was established under the 1978 Reorganization Plan No. 3 and was activated by President Jimmy Carter in an Executive Order on April 1, 1979.
In July, Carter signed Executive Order 12148 shifting disaster relief efforts to the new federal-level agency. FEMA absorbed the Federal Insurance Administration, the National Fire Prevention and Control Administration, the National Weather Service Community Preparedness Program, the Federal Preparedness Agency of the General Services Administration and the Federal Disaster Assistance Administration activities from HUD. FEMA was also given the responsibility for overseeing the nation's Civil Defense, a function which had previously been performed by the Department of Defense's Defense Civil Preparedness Agency.
One of the disasters FEMA responded to was the dumping of toxic waste into Love Canal in Niagara Falls, New York, in the late 1970s. FEMA also responded to the Three Mile Island nuclear accident where the nuclear-generating station suffered a partial core meltdown. These disasters, while showing the agency could function properly, also uncovered some inefficiencies.[citation needed]
In 1993, President Bill Clinton appointed James Lee Witt as FEMA Director. In 1996, the agency was elevated to cabinet rank;[15] this was not continued by President George W. Bush.[16] Witt initiated reforms that would help to streamline the disaster recovery and mitigation process. The end of the Cold War also allowed the agency's resources to be turned away from civil defense to natural disaster preparedness.[12]
After FEMA's creation through reorganization and executive orders, Congress continued to expand FEMA's authority by assigning responsibilities to it. Those responsibilities include dam safety under the National Dam Safety Program Act; disaster assistance under the Stafford Disaster Relief and Emergency Assistance Act; earthquake hazards reduction under the Earthquake Hazards Reduction Act of 1977 and further expanded by Executive Order 12699, regarding safety requirements for federal buildings and Executive Order 12941, concerning the need for cost estimates to seismically retrofit federal buildings; emergency food and shelter under the Stewart B. McKinney Homeless Assistance Act of 1987; hazardous materials, under the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.
In addition, FEMA received authority for counterterrorism through the Nunn-Lugar-Domenici amendment under the Weapons of Mass Destruction Act of 1996, which was a response to the recognized vulnerabilities of the U.S. after the sarin gas attack on the Tokyo subway in 1995.[14]
Congress funded FEMA through a combination of regular appropriations and emergency funding in response to events.[17]
FEMA under Department of Homeland Security (2003–present)
[edit]
Following the attacks of September 11, 2001, Congress passed the Homeland Security Act of 2002, which created the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to better coordinate among the different federal agencies that deal with law enforcement, disaster preparedness and recovery, border protection and civil defense. FEMA was absorbed into DHS effective March 1, 2003.[18] As a result, FEMA became part of the Emergency Preparedness and Response Directorate of Department of Homeland Security, employing more than 2,600 full-time employees. It became Federal Emergency Management Agency again on March 31, 2007, but remained in DHS.[19]
President Bush appointed Michael D. Brown as FEMA's director in January 2003. Brown warned in September 2003 that FEMA's absorption into DHS would make a mockery of FEMA's new motto, "A Nation Prepared", and would "fundamentally sever FEMA from its core functions", "shatter agency morale" and "break longstanding, effective and tested relationships with states and first responder stakeholders". The inevitable result of the reorganization of 2003, warned Brown, would be "an ineffective and uncoordinated response" to a terrorist attack or a natural disaster.[20]
Hurricane Katrina in 2005 demonstrated that the vision of further unification of functions and another reorganization could not address the problems FEMA had previously faced. The "Final Report of the Select Bipartisan Committee to Investigate the Preparation for and Response to Hurricane Katrina", released February 15, 2006, by the U.S. Government Printing Office, revealed that federal funding to states for "all hazards" disaster preparedness needs was not awarded unless the local agencies made the purposes for the funding a "just terrorism" function.[21] Emergency management professionals testified that funds for preparedness for natural hazards were given less priority than preparations for counter-terrorism measures. Testimony also expressed the opinion that the mission to mitigate vulnerability and prepare for natural hazard disasters before they occurred had been separated from disaster preparedness functions, making the nation more vulnerable to known hazards, like hurricanes.[22]
After allegations of mismanagement during Hurricane Katrina, the National Disaster Medical System (NDMS) was transferred from the Department of Homeland Security to the Department of Health and Human Services by the Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness Act, signed by President George W. Bush on December 18, 2006.
In fall 2008, FEMA took over coordination of the Ready Campaign, the national public service advertising campaign in collaboration with the Ad Council, to educate and empower Americans to prepare for and respond to emergencies including natural and man-made disasters. The Ready Campaign and its Spanish-language version Listo asks individuals to do three things: build an emergency supply kit,[23] make a family emergency plan[24] and be informed about the different types of emergencies that can occur and how to respond.[25] The campaign messages have been promoted through television, radio, print, outdoor and web PSAs,[26] as well as brochures, toll-free phone lines and the English and Spanish language websites.
The Post-Katrina Emergency Management Reform Act of 2006 added a Surge Capacity Force, which allows the Department of Homeland Security to supplement FEMA employees with additional personnel from various federal departments in the event the agency is overwhelmed. The Force has been activated for Hurricane Sandy, Hurricane Harvey, Hurricane Irma, Hurricane Maria, and the 2017 California wildfires.[27]
The Stafford Act was amended by the Pets Evacuation and Transportation Standards Act (PETS Act) in 2006, and the Disaster Recovery Reform Act (DRRA) in 2018.
FEMA was put in charge of procuring medical supplies during the COVID-19 pandemic.[28]
According to a tweet posted on April 12, 2022, by Deanne Criswell, the FEMA flag, used between 1981 and 2003, was reintroduced.
Organization
[edit]During the debate of the Homeland Security Act of 2002, some called for FEMA to remain as an independent agency. Following the failed response to Hurricane Katrina, critics called for FEMA to be removed from the Department of Homeland Security.[29] Today FEMA exists as a major agency of the Department of Homeland Security. The Administrator for Federal Emergency Management reports directly to the Secretary of Homeland Security. In March 2003, FEMA joined 22 other federal agencies, programs and offices in becoming the Department of Homeland Security. The new department, headed by Secretary Tom Ridge, brought a coordinated approach to national security from emergencies and disasters – both natural and man-made.
FEMA manages the National Flood Insurance Program. Other programs FEMA previously administered have since been internalized or shifted under direct DHS control.
FEMA is also home to the National Continuity Programs Directorate (formerly the Office of National Security Coordination). ONSC was responsible for developing, exercising, and validating agency-wide continuity of government plans as well as overseeing and maintaining continuity readiness including the Mount Weather Emergency Operations Center. ONSC also coordinated the continuing efforts of other Federal Executive Agencies.
FEMA began administering the Center for Domestic Preparedness in 2007.
FEMA administers the Homeland Security Grant Program (HSGP) which provides funding to state governments, local governments, Tribal governemnts, and Territorial governments along with specified Urban Areas and counties along international borders to invest in security enhancements. HSGP is broken out into three primary grant programs: State Homeland Security Grant Program (SHSP), Urban Area Security Initiative (UASI), and Operation Stonegarden (OPSG). As of 2024, the Tribal Homeland Security Grant Program (THSGP) is funded as a percentage carveout of HSGP as well. The Nonprofit Security Grant Program (NSGP) used to be funded under the HSGP as well, but Congress now funds that program separate from HSGP. NSGP provides funding for nonprofit organizations more at risk to terrorist actions and domestic violence extremeism to invest in target hardening. This includes, but is not limited to, organizations such as educational facilities, hospitals, and house of worship. In 2024, FEMA administered over $3 billion across the suite of homeland security grants.[30][31][32][33][34]
Budget
[edit]In 2018, FEMA had an annual budget of $18 billion[35] that is used and distributed in different states according to the emergencies that occur in each one. An annual list of the use of these funds is disclosed at the end of the year on FEMA's website.[36][37][38][39]
Regions
[edit]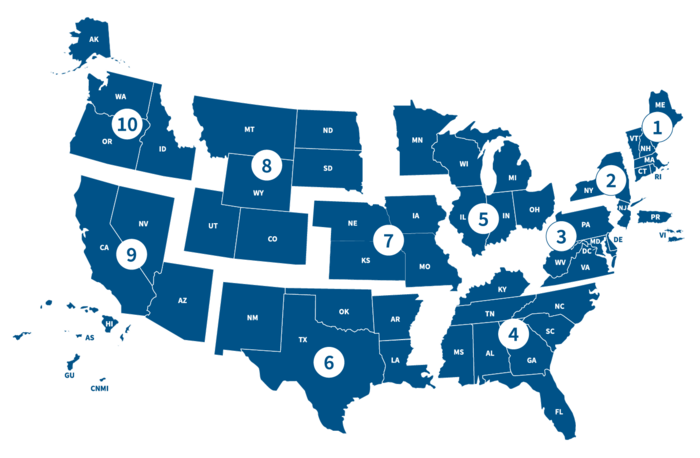
- Regional map[40]
- Region 1, Boston, MA – Serving CT, MA, ME, NH, RI, VT
- Region 2, New York, NY Serving NJ, NY, PR, USVI
- Region 3, Philadelphia, PA Serving DC, DE, MD, PA, VA, WV
- Region 4, Atlanta, GA Serving AL, FL, GA, KY, MS, NC, SC, TN
- Region 5, Chicago, IL Serving IL, IN, MI, MN, OH, WI
- Region 6, Denton, TX Serving AR, LA, NM, OK, TX
- Region 7, Kansas City, MO Serving IA, KS, MO, NE
- Region 8, Denver, CO Serving CO, MT, ND, SD, UT, WY
- Region 9, Oakland, CA Serving AZ, CA, HI, NV, GU, AS, CNMI, RMI, FM
- Region 10, Bothell, WA Serving AK, ID, OR, WA
Cadres
[edit]FEMA maintains 23 cadres of various work functions and skillsets to prepare, respond, and recover from various disasters.[41]
- Acquisitions (ACQ)
- Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
- Civil Rights (CVR)
- Disability Integration (DI)
- Disaster Emergency Communications (DEC)
- Disaster Field Training Operations (DFTO)
- Disaster Survivor Assistance (DSA)
- Enviromental/Historic Preservation (EHP)
- External Affairs (EA)
- Field Leadership (FL)
- Financial Management (FM)
- Hazard Mitigation (HM)
- Human Resources (HR)
- Individual Assistance (IA)
- Information Technology (IT)
- Interagency Recovery Coordination (IRC)
- Logistics (LOG)
- Office of Chief Counsel, Legal Affairs (OCC)
- Operations (OPS)
- Planning (PLAN)
- Public Assistance (PA)
- Safety (SAF)
- Security (SEC)
Pre-disaster mitigation programs
[edit]FEMA's Mitigation Directorate[42] is responsible for programs that take action before a disaster, in order to identify risks and reduce injuries, loss of property, and recovery time.[43] The agency has major analysis programs for floods, hurricanes and tropical storms, dams, and earthquakes.[43][44]
FEMA works to ensure affordable flood insurance is available to homeowners in flood plains, through the National Flood Insurance Program, and also works to enforce no-build zones in known flood plains and relocate or elevate some at-risk structures.[45]
Pre-Disaster Mitigation grants are available to acquire property for conversion to open space, retrofit existing buildings, construct tornado and storm shelters, manage vegetation for erosion and fire control, and small flood control projects.[46] Critics say this program is underperforming because it is starved for funding compared to disaster response and recovery, the process of applying for a buyout is unreasonably slow, and is wasting taxpayer dollars because the National Flood Insurance Program has paid to reconstruct some properties up to 18 times.[47] 1% of NFIP-insured properties are responsible for more than one quarter of the money the program has paid out.[48]
The Hazard Mitigation Grant Program funds rebuilding after a current disaster in a way that reduces the impact of a similar future disaster.[49]
Response capabilities
[edit]
FEMA's emergency response is based on small, decentralized teams trained in such areas as the National Disaster Medical System (NDMS), Urban Search and Rescue (USAR), Disaster Mortuary Operations Response Team (DMORT), Disaster Medical Assistance Team (DMAT), and Mobile Emergency Response Support (MERS).
National Response Coordination Center (NRCC)
[edit]FEMA's National Response Coordination Center (NRCC) is a multiagency center located at FEMA HQ that coordinates the overall Federal support for major disasters and emergencies, including catastrophic incidents in support of operations at the regional level. The FEMA Administrator,[52] or his or her delegate, activates the NRCC in anticipation of, or in response to, an incident by activating the NRCC staff, which includes FEMA personnel, the appropriate Emergency Support Functions, and other appropriate personnel (including nongovernmental organization and private sector representatives). During the initial stages of a response, FEMA will, as part of the whole community, focus on projected, potential, or escalating critical incident activities. The NRCC coordinates with the affected region(s) and provides needed resources and policy guidance in support of incident-level operations. The NRCC staff specifically provides emergency management coordination, planning, resource deployment, and collects and disseminates incident information as it builds and maintains situational awareness—all at the national-level.[53] FEMA maintains the NRCC as a functional component of the NOC for incident support operations.[54][55]
An example of NRCC activity is the coordination of emergency management activities that took place in connection with the 2013 Colorado floods.[56]
Disaster Medical Assistance Teams
[edit]
Disaster Medical Assistance Teams (DMAT) provide medical care at disasters and are typically made up of doctors and paramedics. There are also National Nursing Response Teams (NNRT), National Pharmacy Response Teams (NPRT) and Veterinary Medical Assistance Teams (VMAT). Disaster Mortuary Operational Response Teams (DMORT) provide mortuary and forensic services. National Medical Response Teams (NMRT) are equipped to decontaminate victims of chemical and biological agents.
Urban Search and Rescue (US&R)
[edit]The Urban Search and Rescue Task Forces perform rescue of victims from structural collapses, confined spaces, and other disasters, for example, mine collapses and earthquakes.
Mobile Emergency Response Support (MERS)
[edit]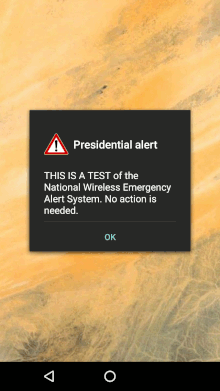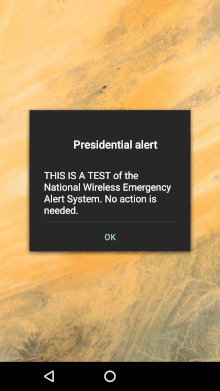

These teams provide communications support to local public safety. For instance, they may operate a truck with satellite uplink, computers, telephone, and power generation at a staging area near a disaster so that the responders can communicate with the outside world. There are also Mobile Air Transportable Telecommunications System (MATTS) assets which can be airlifted in. Also, portable cell phone towers can be erected to allow local responders to access telephone systems.
The first test of the national wireless emergency system by FEMA was broadcast to an estimated 225 million electronic devices at 14:18 EDT on October 3, 2018. The text message was accompanied by a flashing warning sign and warning tone. The president may direct FEMA to broadcast such alerts only for national emergencies or if the public is in danger. The facility may not be used for personal messages from the president. Mobile phone owners can not opt out of these warnings.[57][58]
Preparedness for nuclear incidents
[edit]On August 1, 2008, FEMA released "Planning Guidance for Protection and Recovery Following Radiological Dispersal Device (RDD) and Improvised Nuclear Device (IND) incidents",[59] which provide an action guide in the case of radioactive contamination. This guidance is specified as action guide for Radiological Dispersal Devices (RDD) and Improvised Nuclear Devices (IND) involving high levels of radiation. According to the Federation of American Scientists, during the Cold War FEMA prepared assessments of the likely consequences of a full-scale Soviet nuclear attack on the United States for use in planning mitigation and recovery efforts.[60] FEMA also prepared plans for evacuating major U.S. cities in response to a nuclear war, dubbed CRP-2B.[61]
Training
[edit]FEMA offers a large number of training classes, either at its own centers, through programs at the state level, in cooperation with colleges and universities, or online. The latter are free classes available to anyone, although only those with U.S. residency or work eligibility can take the final examinations. More information is available on the FEMA website under the "Emergency Personnel" and "Training" subheadings. Other emergency response information for citizens is also available at its website.
FEMA runs the Incident Workforce Academy, a two-week emergency preparedness training program for FEMA employees. The first class of the academy graduated in early 2014.[62]
The Training and Education Division within FEMA's National Integration Center directly funds training for responders and provides guidance on training-related expenditures under FEMA's grant programs. Information on designing effective training for first responders is available from the Training and Education Division. Emergency managers and other interested members of the public can take independent study courses for certification at FEMA's online Emergency Management Institute.
Emergency Management Institute training and certifications
[edit]EMI offers credentials and training opportunities for United States Citizens. Note that students do not have to be employed by FEMA or be a federal employee for some of the programs. However, they do need to create a FEMA SID to take the final exams[63]
EMI maintains a strategic partnership with Frederick Community College. FCC has contracted with the Emergency Management Institute to provide college credit for the Independent Study Program (ISP). FCC offers eight specialized Letters of Recognition, an Undergraduate Certificate, and an Associate of Applied Science degree in Emergency Management.[64]
FEMA Corps
[edit]FEMA Corps, who range in age from 18 to 26 years old, is a cadre dedicated to disaster response and recovery. It is a new partnership between The Corporation for National and Community Service's AmeriCorps NCCC (National Civilian Community Corps) and FEMA.[65] The Corps, described as a "dedicated, trained, and reliable disaster workforce", works full-time for 10 months on federal disaster response, recovery, mitigation, and preparedness efforts across numerous sections. Over 150 members of the inaugural FEMA Corps class graduated in June 2013, at the Southern Region AmeriCorps NCCC campus in Vicksburg, Mississippi. The Pacific Region campus in Sacramento, California and the Southern Region campus both support a FEMA Corps class annually.[66] The Corps work on teams of 6 to 10 people and follow the traditional NCCC model of living together and traveling together. In addition to working with FEMA, Corps members must perform AmeriCorps responsibilities such as Physical Training three times a week, National Days of Service, and Individual Service Projects in communities throughout the United States. Members receive $6.10 a day for food ($15 a day when deployed to on disaster project) and a living stipend of approximately $3,500 over 10 months (Approximately $175 every two weeks). Team leaders receive a larger stipend of approximately $10,000 over the course of 10 months (Approximately $500 every two weeks). The Segal AmeriCorps education award is distributed to Corps members who successfully finish their term of service, completing 1,700 or more total hours. The amount of a full-time Segal AmeriCorps Education Award is equivalent to the maximum value of the Pell Grant for the fiscal year in which the term of national service is approved, and can therefore change between different classes.[67][68]

Donations management
[edit]FEMA has led a Public-Private Partnership in creating a National Donations Management Program making it easier for corporations or individuals not previously engaged to make offers of free assistance to States and the Federal Government in times of disaster. The program is a partnership among FEMA, relief agencies, corporations/corporate associations and participating state governments.[citation needed]
Criticisms
[edit]Hurricane Andrew
[edit]In August 1992, Hurricane Andrew struck the Florida and Louisiana coasts with 165 mph (265 km/h) sustained winds. FEMA was widely criticized for its response to Andrew, summed up by the famous exclamation, "Where in the hell is the cavalry on this one?" by Kate Hale, emergency management director for Miami-Dade County, Florida. FEMA and the federal government at large were accused of not responding fast enough to house, feed and sustain the approximately 250,000 people left homeless in the affected areas. Within five days the federal government and neighboring states had dispatched 20,000 National Guard and active duty troops to South Dade County to set up temporary housing. This event and FEMA's performance was reviewed by the National Academy of Public Administration in its February 1993 report "Coping With Catastrophe" which identified several basic paradigms in Emergency Management and FEMA administration that were causes of the failed response.
FEMA had previously been criticized for its response to Hurricane Hugo, which hit South Carolina in September 1989, and many of the same issues that plagued the agency during Hurricane Andrew were also evident during the response to Hurricane Katrina in 2005.
Additionally, upon incorporation into DHS, FEMA was legally dissolved and a new Emergency Preparedness and Response Directorate was established in DHS to replace it. Following enactment of the Post-Katrina Emergency Management Reform Act of 2006 FEMA was reestablished as an entity within DHS, on March 31, 2007.
Southern Florida hurricanes
[edit]South Florida newspaper Sun-Sentinel has an extensive list of documented criticisms of FEMA during the four hurricanes that hit the region in 2004.[69] Some of the criticisms include:
- When Hurricane Frances hit South Florida on Labor Day weekend (over 100 miles north of Miami-Dade County), 9,800 Miami-Dade applicants were approved by FEMA for $21 million in storm claims for new furniture; clothes; thousands of new televisions, microwaves and refrigerators; cars; dental bills; and a funeral even though the Medical Examiner recorded no deaths from Frances. A U.S. Senate committee and the inspector general of the Department of Homeland Security found that FEMA inappropriately declared Miami-Dade county a disaster area and then awarded millions, often without verifying storm damage or a need for assistance.[70][71]
- FEMA used hurricane aid money to pay funeral expenses for at least 203 Floridians whose deaths were not caused by the 2004 hurricanes, the state's coroners have concluded. Ten of the people whose funerals were paid for were not in Florida at the time of their deaths.[72]
The rising sea levels, global temperatures, and increase of flooding and severe storms has called for a change within the procedure of flood insurance. The communities that are directly impacted by these changes include coastal communities and waterfront homes. The procedural design of flood insurance is done through FEMA’s (Federal Emergency Management Agency) National Flood Insurance Program. Previously the Insurance Program created in 1968 was constructed around the "100-year floodplain" which is the "area that would be inundated by the 100-year flood, better thought of as an area that has a one percent or greater chance of experiencing a flood in any single year",[73] and large subsidies for coastal homes, especially in Florida. However, in 2019, major changes were made, and the new program called Risk Rating 2.0 was introduced, which prices a house on its individual flood risk.[74] It will account for the distance one's house is from a flood source, the types and frequency of flooding, and characteristics of the cost to rebuild. This new program will greatly impact states like Florida that have intense risk of hurricanes and sea level rise. Through the initial program, the homes on the coast were mostly being subsidized at the cost of the homeowners more inland, and more likely lower-income and people of color.[citation needed] However, as previously stated, with Risk Rating 2.0, homeowners in higher risk areas of greater flooding will be paying for that risk through insurance, and with that may come with re-evaluating the longevity of one's place on the coasts of Florida. On the other hand, with FEMA's program as a national program, we[who?] see different impacts in places like New England.[75] It has been indicated that states like Maine will be greatly impacted positively by the new program. The bays, inlets, and coves are proved to be good protective measures for most waterfront properties. In addition to Maine, states like Iowa and Nebraska will see impacts to their flood insurance policies. It is stated that almost 50% of Nebraskans and 40% of Iowans will see a decrease in their policies.[76] Overall we[who?] see many different types of complications to this new set-up, such as retirees on fixed incomes, long-term mortgages, and depreciation of household value. As this program is relatively new, impacts of the program will continue to be seen in the following years.
Hurricane Katrina
[edit]
FEMA received intense criticism for its response to the Hurricane Katrina disaster in August 2005. FEMA had pre-positioned response personnel in the Gulf Coast region. However, many could not render direct assistance and were able to report only on the dire situation along the Gulf Coast, especially from New Orleans. Within three days, a large contingent of National Guard and active duty troops were deployed to the region.
The enormous number of evacuees simply overwhelmed rescue personnel. The situation was compounded by flood waters in the city that hampered transportation and poor communication among the federal government, state, and local entities. FEMA was widely criticized for what is seen as a slow initial response to the disaster and an inability to effectively manage, care for, and move those who were trying to leave the city.
Then-FEMA Director Michael D. Brown was criticized personally for a slow response and an apparent disconnection with the situation. Brown would eventually be relieved of command of the Katrina disaster and soon thereafter resigned.
According to the U.S. House of Representatives Select Bipartisan Committee to Investigate the Preparation for and Response to Hurricane Katrina:[77]
- "The Secretary Department of Homeland Security should have designated the Principal Federal Official on Saturday, two days prior to landfall, from the roster of PFOs who had successfully completed the required training, unlike then FEMA Director Michael Brown. Considerable confusion was caused by the Secretary's PFO decisions."
- "DHS and FEMA lacked adequate trained and experienced staff for the Katrina response."
- "The readiness of FEMA's national emergency response teams was inadequate and reduced the effectiveness of the federal response."
- "Long-standing weaknesses and the magnitude of the disaster overwhelmed FEMA's ability to provide emergency shelter and temporary housing."
- "FEMA logistics and contracting systems did not support a targeted, massive, and sustained provision of commodities."
- "Before Katrina, FEMA suffered from a lack of sufficiently trained procurement professionals."

Other failings were also noted. The Committee devoted an entire section of the report to listing the actions of FEMA.[78] Their conclusion was:
For years emergency management professionals have been warning that FEMA's preparedness has eroded. Many believe this erosion is a result of the separation of the preparedness function from FEMA, the drain of long-term professional staff along with their institutional knowledge and expertise, and the inadequate readiness of FEMA's national emergency response teams. The combination of these staffing, training, and organizational structures made FEMA's inadequate performance in the face of a disaster the size of Katrina all but inevitable.[78]
Pursuant to a temporary restraining order issued by Hon. Stanwood R. Duval, United States District Court Judge, Eastern District of Louisiana as a result of the McWaters v. FEMA class-action, February 7, 2006, was set as the deadline for the official end of any further coverage of temporary housing costs for Katrina victims.[79][80]
After the February 7 deadline, Katrina victims were left to their own devices either to find permanent housing for the long term or to continue in social welfare programs set up by other organizations. There were many Katrina evacuees living in temporary shelters or trailer parks set up by FEMA and other relief organizations in the first months after the disaster hit, but much more were still unable to find housing.
In July 2007, ice that had been ordered for Katrina victims but had never been used and kept in storage facilities, at a cost of $12.5 million, was melted down.[81]
In June 2008, a CNN investigation found that FEMA gave away about $85 million in household goods meant for Hurricane Katrina victims to 16 other states.[82]
Buffalo snowstorm
[edit]FEMA came under attack for their response to the October Surprise Storm in Buffalo, New York, on October 13, 2006. As FEMA legally cannot interfere with state business unless asked, FEMA responded that as per procedure, the governor of the state of New York, George Pataki, had not asked for FEMA's assistance. FEMA Headquarters had been in constant contact with State congressional offices providing them with the latest information available. Claims state that FEMA officials did not arrive until October 16, three days after the storm hit. The snowstorm damage by this time included downed power wires, downed trees, and caused structural damage to homes and businesses.[83]
Dumas, Arkansas, tornadoes
[edit]Many people of Dumas, Arkansas, especially victims of tornadoes on February 24, 2007, criticized FEMA's response in not supplying the number of new trailers they needed, and sending only a set of used trailers, lower than the needed quantity. Following the storm, U.S Senator Mark Pryor had criticized FEMA's response to the recovery and cleanup efforts.[84]
California wildfires
[edit]FEMA came under intense criticism when it was revealed that a press conference on the October 2007 California wildfires was staged. Deputy Administrator Harvey E. Johnson was answering questions from FEMA employees who were posing as reporters. Many of these questions were "softball" questions (i.e., "Are you happy with FEMA's response so far?"), intentionally asked in a way that would evoke a positive response giving the impression that FEMA was doing everything right. In this way, any scrutiny from real reporters (many of whom were given only a 15-minute notice) would have been avoided. Fox News, MSNBC, and other media outlets aired the staged press briefing live.[85] Real reporters were notified only 15 minutes in advance and were able to call into only a conference line, which was set to "listen-only" mode. The only people there were primarily FEMA public affairs employees.[86]
Hurricane Maria
[edit]In September 2017, Hurricane Maria struck Dominica and Puerto Rico with 175 mph (280 km/h) sustained winds. Maria was the fifth-strongest storm to ever strike the United States with stronger winds than those brought by Irma and similar rain brought to Houston by Hurricane Harvey.[87] Despite FEMA's preemptive efforts in Puerto Rico, the island was still devastated beyond expectation. The agency had prepared some provisions for displaced residents before the storm struck, including: roughly 124 FEMA staff members being positioned on the island, food, water, and bedding.[87] However, people reported the FEMA food packages were unhealthy snacks such as the confectionery Skittles.[88] FEMA was widely criticized for its response to Maria, as the island quickly fell into a humanitarian crisis.[89][90]
The island also experienced a massive loss of power as a result of flood and wind damage sustained during Maria. In the beginning of October 2017, Lieutenant General Todd Semonite, chief and commanding general of the United States Army Corps of Engineers, explained the extent of and necessity of aid for this power crisis. Semonite described some specifics of the outage to reporters, explaining that the island requires "2,700 megawatts of electricity to operate and at last count had 376 megawatts available." This translates to about 14 percent of the grid being functional.[91]
FEMA Administrator William "Brock" Long told reporters in a briefing following the storm that Puerto Rico politics had hindered the ability of the federal government to send aid. He explained that political divisions had prevented unity for leaders in this time of crisis, describing that their issue was "even worse" than the mainland United States' issue between Democrats and Republicans. Residents, in some cases, were required to fill out paperwork in English rather than Spanish with little to no hope of receiving the aid they had requested.[91]
Brigadier General Jose Reyes of the Puerto Rico National Guard discussed a strategy to quicken the arrival of resources via the Port of Ponce, located on the southern coast of Puerto Rico.[92] Reyes also attributed the delay in these services to the unprecedented series of storms that demanded attention from the agency within a short period of time. Regarding this, General Reyes told reporters " We were not even getting back on our feet after Irma, then suddenly we got hit by Maria." He also addressed the disparities between aid sent to mainland disaster-stricken areas and Puerto Rico, explaining that in areas such as Florida and Texas, who had recently struck with similar damages, transportation of resources is relatively simpler. This is because they are able to utilize infrastructure to transport aid. Transporting similar resources to Puerto Rico has proved to be more difficult, as they must travel across the ocean, either in aircraft or in ships.[91] Long also mentioned that Puerto Rico's international airport was not able to operate at full capacity, which posed an additional obstacle for federal aid imports.
Long resigned on March 8, 2019, following criticism of his handling of Hurricane Maria and an ethical complaint over misuse of official vehicles, costing $151,000.[93] Homeland Security Secretary Kirstjen Nielsen said that Long would have to reimburse the government for the cost of the vehicles and staff involved in the trips, many of which were between Washington and his home in North Carolina. Nielsen submitted her own resignation as Secretary of Homeland Security less than a month later on April 7, 2019.[94]
Hurricane Harvey
[edit]Hurricane Harvey made landfall in late August 2017 as a Category 4 Hurricane with 130 mph (215 km/h) sustained winds. The Hurricane predominantly affected southeast Texas; however, its effects were felt as far as Arkansas, Kentucky, and Tennessee in the form of flash flooding.[95] Harvey slowly progressed around southeast Texas, where it produced heavy precipitation over the region. This caused heavy flooding in residential areas such as Colorado City, Liberty, and Montgomery, Texas.[95][96]
Harvey was the first of a series of hurricanes and tropical storms to affect the United States between August and September 2017. The effects of these storms included extreme flooding, damage from high speed winds, structural damage, and humanitarian concerns regarding the availability of basic necessities such as food, water, and shelter.[97][98]
Some recipients were forced to wait up to two months before receiving aid from FEMA, as technical complications held up both their application for it and the processing of said applications. Some residents were denied Federal Aid and have to dispute their denial in efforts to rebuild and repair properties without taking a considerably large financial loss.
Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19)
[edit]In early April 2020, the Los Angeles Times reported that the Trump administration was "quietly" seizing medical supplies from states and hospitals, citing hospital and clinic officials catering to seven states. These officials stated that the administration has not informed them how they can otherwise get access to their ordered supplies. A FEMA representative said the agency, working with the Department of Health and Human Services and the Department of Defense, has developed a system for identifying needed supplies from vendors and distributing them equitably. The federal government also seized an order for thermometers meant for Florida, an order for masks from the Texas Association of Community Health Centers, and an order for testing supplies meant for the PeaceHealth hospital system in Washington, Oregon and Alaska.[99]
On April 24, San Francisco Mayor London Breed said "We've had situations when things we've ordered that have gone through Customs were confiscated by FEMA to be diverted to other locations. We know everyone is dealing with a serious challenge. Through Customs, we've had situations where those items have been taken and put out on the market for the highest bidder, putting cities against cities and states against states."[100]
Massachusetts Secretary of Health and Human Services Marylou Sudders cited a shipment of 3 million masks that the state had negotiated to buy from BJ's Wholesale Club, until the federal government impounded them from the Port of New York and New Jersey on March 18. A further order from MSC Industrial Supply for 400 masks to be delivered on March 20 was also claimed by the federal government using force majeure.[101] Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker reached out to the New England Patriots professional American football team, who used the team plane "AirKraft" to bring approximately 1.2 million N95 masks from China to Boston.[102]
In late April, reports of the actions taken by FEMA in Massachusetts prompted Maryland Governor Larry Hogan to deploy the Maryland National Guard and task them with guarding a shipment of 500,000 COVID-19 testing kits purchased from South Korean company LabGenomics by the Government of Maryland.[103][104][105] The tests were subsequently held in an "undisclosed location," under the continued supervision of the Maryland National Guard.
The state of Colorado was set to purchase 500 ventilators before Federal Emergency Management Agency swooped in and bought them first. President Trump announced on Twitter that the federal government would be sending 100 ventilators to Colorado at the request of Senator Cory Gardner.[106] The incident caused Colorado Governor Polis to make future supply purchases in secret.[107]
In late April, 5,000,000 masks meant for hospitals of the Veterans Health Administration were seized by FEMA and redirected to the Strategic National Stockpile, stated Richard Stone, Executive in Charge, Veterans Health Administration.[108] After an appeal from Veterans Affairs Secretary Robert Wilkie to FEMA, the agency provided the VA with 500,000 masks.[108]
Federalism and FEMA
[edit]The costs of a disaster to states and localities can escalate quickly. Federal assistance becomes fully available with the approval of the President and at the request of the governor. Public help for governments to repair facilities is 75% federally funded with local governments responsible for covering the rest (unless the state grants aid or loans). FEMA does not compensate for buildings that have been improperly maintained by the state or local government nor does it pay to upgrade or improve facilities. FEMA coordinates but does not fund disaster assistance provided by the Small Business Administration or the Farmers Home Administration. FEMA grant-in aid funds come from revenue sharing, the Department of Housing and Urban Development and the Department of Transportation. Grants for disaster preparedness can be used by flood control districts.[109]
Many states have disaster relief agencies of their own. In the event of a disaster outside of a state's operating capacity, the director of said agency will advise the Governor whether or not to proclaim a state of emergency. Declaring a state of emergency, upon Presidential approval, entitles a state to federal assistance.
Proclaiming a state of emergency does not guarantee federal assistance. States also rely on mutual aid agreements, such as the Civil Defense and Disaster Compact and Emergency Management Assistance Compact. A mutual aid agreement can be between neighboring states, cities, counties and cities, states and cities or an entire region. These agreements allow agencies to share resources so they are better prepared for emergencies.[109]
Local governments have the most immediate responsibility. Four factors shape local disaster response:
- The extent of tax base depletion
- The scope of lost sales tax revenue
- Access to other forms of revenue
- Amount of city debt
Having a mostly intact tax base allows local governments to maintain steady revenue stream. Business unharmed by a disaster will be able to continue to generate sales tax revenue. Cities with access to large revenue reserves and strong mutual aid agreements will have greater response capacity. While cities with large municipal debt that would be unable to pay back state or federal loans would be in a difficult situation.[110]
U.S. v. Parish of Jefferson et al
[edit]This case gave FEMA the right to sue in order to recover funds paid out in flood insurance claims for flood damage as a result of poor decisions by local officials and developers. The case also gave FEMA the power to sue localities who fail to meet flood plain management requirements.[110]
List of FEMA heads
[edit]| Portrait | Name | Start | End | President | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
James Hafer | May 1975 | April 1, 1979 | Gerald Ford (1974–1977) | |

|
Gordon Vickery Acting |
April 1, 1979 | July 1979 | Jimmy Carter (1977–1981) | |

|
Thomas Casey Acting |
July 1979 | August 1979 | ||

|
John Macy | August 1979 | January 20, 1981 | ||

|
Bernard Gallagher Acting |
January 20, 1981 | April 1981 | Ronald Reagan (1981–1989) | |

|
John McConnell Acting |
April 1981 | May 1981 | ||

|
Jeff Giuffrida | May 1981 | September 1, 1985 | ||

|
Robert Morris Acting |
September 1, 1985 | November 1985 | ||

|
Julius Becton | November 1985 | June 1989 | ||

|
Robert Morris Acting |
June 1989 | May 1990 | George H. W. Bush (1989–1993) | |

|
Jerry Jennings Acting |
May 1990 | August 1990 | ||

|
Wallace Stickney | August 1990 | January 20, 1993 | ||

|
William Tidball Acting |
January 20, 1993 | April 5, 1993 | Bill Clinton (1993–2001) | |

|
James Witt | April 5, 1993 | January 20, 2001 | ||

|
John Magaw Acting |
January 20, 2001 | February 15, 2001 | George W. Bush (2001–2009) | |

|
Joe Allbaugh | February 15, 2001 | April 15, 2003 | ||

|
Michael Brown | April 15, 2003 | September 12, 2005 | ||

|
David Paulison | September 12, 2005 Acting: September 12, 2005 – June 8, 2006 |
January 21, 2009 | ||

|
Nancy Ward Acting |
January 21, 2009 | May 19, 2009 | Barack Obama (2009–2017) | |

|
Craig Fugate | May 19, 2009 | January 20, 2017 | ||

|
Bob Fenton Acting |
January 20, 2017 | June 23, 2017 | Donald Trump (2017–2021) | |

|
Brock Long | June 23, 2017 | March 8, 2019 | ||

|
Pete Gaynor | March 8, 2019 Acting: March 8, 2019 – January 14, 2020 |
January 12, 2021 | ||

|
Bob Fenton Acting |
January 12, 2021 | April 26, 2021 | Joe Biden (2021–2025) | |

|
Deanne Criswell | April 26, 2021 | present | ||
Titles
[edit]- Director of the Office of Emergency Preparedness within the General Services Administration (May 1975 – April 1, 1979)
- Director of Federal Emergency Management Agency as an independent agency (April 1, 1979 – April 15, 2003)
- Elevated to Cabinet-level (February 26, 1996 – January 20, 2001)[15][16]
- Director of Federal Emergency Management Agency and Under Secretary of Homeland Security for Emergency Preparedness and Response within the Department of Homeland Security (April 15, 2003 – June 8, 2006)
- Director of Federal Emergency Management Agency and Under Secretary of Homeland Security for Federal Emergency Management within the Department of Homeland Security (June 8, 2006 – March 31, 2007)
- Administrator of Federal Emergency Management Agency within the Department of Homeland Security (March 31, 2007 – present)
See also
[edit]- History of homeland security in the United States
- United States civil defense
- Federal Civil Defense Authority
- FEMA camps conspiracy theory
- FEMA photo library
- National Emergency Technology Guard
- PDD-62, the National Security Directive defining FEMA's counterterrorism jurisdiction
- Civil defense by country
- Civil Contingencies Secretariat, British counterpart emergency management agency
- Emergency Preparedness Canada, Canadian counterpart emergency management agency
- National Disaster Medical System
- Disaster Medical Assistance Teams
- Disaster Mortuary Operational Response Teams
- Integrated Public Alert and Warning System
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Executive Order 12127—Federal Emergency Management Agency". Federation of American Scientists.
- ^ "FEMA Publication 1" (PDF). FEMA. Federal Emergency Management Agency. Retrieved September 18, 2023.
- ^ "Procedures Relating to a Lapse in Appropriations" (PDF). www.fema.gov. Department of Homeland Security. September 22, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2023.
- ^ "DHS FEMA Budget Overview FY 2023 Congressional Justification" (PDF). FEMA. Archived from the original on September 18, 2023. Retrieved September 18, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Shelter and Services Program". Fema.gov. Retrieved December 19, 2024.
- ^ "The Federal Emergency Management Agency" (PDF). Fema.gov. November 2010. Retrieved February 3, 2017.
- ^ History of Federal Domestic Disaster Aid Before the Civil War Archived December 14, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Biot Report #379: July 24, 2006. Suburban Emergency Management Project.
- ^ "Guide to House Records: Chapter 23 Ford's Theater Disaster". Archives.gov. Archived from the original on September 21, 2016. Retrieved September 8, 2016.
- ^ Article on the RFC from EH.NET's Encyclopedia. Archived October 29, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ US Fish and Wildlife Service. "Flood Control Act of 1944". Digest of Federal Resource Laws of Interest to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ a b "Records of the Federal Emergency Management Agency [FEMA]". National Archives. U.S. Government. August 15, 2016.
- ^ a b "FEMA History" Archived May 9, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Federal Emergency Management Agency.
- ^ a b c Bea, Keith, "Proposed Transfer of FEMA to the Department of Homeland Security", Order Code RL31510 (updated July 29, 2002), Report for Congress, Congressional Research Service: Library of Congress.
- ^ a b Falkenrath, Richard S., "Problems of Preparedness: U.S. Readiness for a Domestic Terrorist Attack" (2001)International Security, Boston.
- ^ a b "President Clinton Raises FEMA Director to Cabinet Status" (Press release). Federal Emergency Management Agency. February 26, 1996. Archived from the original on January 16, 1997. Retrieved March 3, 2010.
- ^ a b Fowler, Daniel (November 19, 2008). "Emergency Managers Make It Official: They Want FEMA Out of DHS". CQ Politics. Archived from the original on November 29, 2008. Retrieved March 3, 2010.
During the Clinton administration, FEMA Administrator James Lee Witt met with the cabinet. His successor in the Bush administration, Joe M. Allbaugh, did not.
(Archived by WebCite at ) - ^ Murry, Justin (updated July 10, 2006). "Emergency Supplemental Appropriations Legislation for Disaster Assistance: Summary Data FY1989 to FY2006", CRS Report for Congress, Congressional Research Service: The Library of Congress.
- ^ "Should FEMA Remain Part Of Homeland Security?". NPR.org. Retrieved September 21, 2021.
- ^ "Post-Katrina Emergency Management Reform Act of 2006" (PDF). doi.gov. Retrieved September 26, 2024.
- ^ Grunwald, Michael; Glasser, Susan (December 23, 2005). "Brown's Turf Wars Sapped FEMA's Strength". The Washington Post. p. A01. Retrieved April 18, 2007.
- ^ Senate Bipartisan Committee (February 15, 2006), "The Final Report of the Select Bipartisan Committee to Investigate the Preparation for and Response to Hurricane Katrina, U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, D.C.
- ^ Senate Bipartisan Committee, 2006, p. 208.
- ^ "Build A Kit | Ready.gov". Ready.gov. Archived from the original on November 1, 2016. Retrieved October 31, 2016.
- ^ "Make A Plan | Ready.gov". Ready.gov. Retrieved October 31, 2016.
- ^ "About the Ready Campaign | Ready.gov". Ready.gov. Retrieved October 31, 2016.
- ^ "Emergency Preparedness". AdCouncil. Retrieved October 31, 2016.
- ^ "Surge Capacity Force". January 30, 2013. Retrieved June 3, 2021.
- ^ Cole, Devan (March 22, 2020). "Illinois governor says 'it's a wild west' for medical supplies because of Trump's response to states' requests". CNN. Retrieved March 23, 2020.
- ^ Serving America's Disaster Victims: FEMA Where Does it Fit? Archived September 4, 2015, at the Wayback Machine Homeland Security Policy Institute. January 13, 2009.
- ^ Reese, Shawn (October 28, 2016). "Department of Homeland Security Preparedness Grants: A Summary and Issues" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ "Nonprofit Security Grant Program: Summary and Potential Issues for Congress". Congressional Research Service. February 18, 2022. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ Deutch, Gabby (November 6, 2023). "Schumer calls for $1 billion in federal nonprofit security funding". Jewish Insider. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ Beutel, Alejandro (February 15, 2022). "Assessing the Non-Profit Security Grant Program After Colleyville". New Lines Institute. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ Rod, Marc (December 21, 2022). "NSGP funding increase called a positive step, but also disappointing shortfall". Jewish Insider. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ "Department of Homeland Security Federal Emergency Management Agency, Fiscal Year 2018".
- ^ "Hurricane Sandy Anniversary 2014: Billions Of Dollars In Federal Aid Still Unpaid". International Business Times. October 29, 2014.
- ^ "FY2015 FEMA Budget". C-span.org.
- ^ "FEMA Wasted Billions on Administrative Costs". Thefiscaltimes.com.
- ^ "Why New Jersey Got Billions Less Than New York in FEMA Disaster Aid After Sandy – NJ Spotlight". Njspotlight.com. July 9, 2015.
- ^ "Regional Operations | FEMA.gov". Archived from the original on July 15, 2014. Retrieved December 9, 2018.
- ^ "Cadres". Federal Emergency Management Agency. May 7, 2024. Retrieved November 19, 2024.
- ^ "Mitigation". Federal Emergency Management Agency. Archived July 1, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b "FEMA's Mitigation Directorate Fact Sheet". Federal Emergency Management Agency.
- ^ HAZUS Archived July 4, 2012, at the Wayback Machine is a computer model for hurricane, earthquake, and flood damage estimates.
- ^ "FEMA: Severe Repetitive Loss Program". Archived from the original on July 2, 2012. Retrieved February 6, 2016.
- ^ "Grant Program Comparison: Mitigation Division Grant Programs". Archived October 10, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Debt-Laden FEMA Is Slow To Act On Program That Buys Flooded Houses
- ^ Planet Money – Episode 797: Flood Money
- ^ Hazard Mitigation Grant Program (HMGP)
- ^ Annual data: "Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters / United States Billion-Dollar Disaster Events 1980- (CPI-Adjusted)". National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI), part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Archived from the original on January 13, 2024.
- ^ Smith, Adam B.; NOAA National Centers For Environmental Information (December 2020). "Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters: Overview / 2020 in Progress". NCDC.NOAA. National Centers for Environmental Information (NCDC, part of NOAA). doi:10.25921/stkw-7w73. Archived from the original on December 10, 2020. Retrieved December 11, 2020. and "Contiguous U.S. ranked fifth warmest during 2020; Alaska experienced its coldest year since 2012 / 2020 Billion Dollar Disasters and Other Notable Extremes". NCEI.NOAA.gov. NOAA. January 2021. Archived from the original on January 8, 2021. For 2021 data: "Calculating the Cost of Weather and Climate Disasters / Seven things to know about NCEI's U.S. billion-dollar disasters data". ncei.noaa.gov. October 6, 2017. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022.
- ^ "National Response Framework : Second Edition" (PDF). Fema.gov. May 2013. Retrieved October 3, 2018.
- ^ "FEMA's State-of-the-Art National Response Coordination Center". 2002-2009-fpc.state.gov. Archived from the original on March 8, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2016.
- ^ National Response Framework. May 2013. p. 43.
- ^ "National Response Coordination Center: It Takes A Whole Community for Response". Fema.gov. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- ^ "Homeland Security Today: FEMA Monitors Colorado Flooding; Supports State, Local Response". HSToday.us. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- ^ Here’s what Vail learned when it tried out the "Presidential Alert" messaging system FEMA will test Wednesday Denver Post, 2018-10-01.
- ^ "Presidential alert" sounds off on mobile phones nationwide Denver Post, 2018-10-03.
- ^ FEMA, DHS "Planning Guidance for Protection and Recovery Following RDD and IND incidents" Archived May 18, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved July 6, 2011.
- ^ Federal Emergency Management Agency (April 1987). "Nuclear Attack Planning Base - 1990 : Final Project Report (NAPB-90)" – via The Nuclear Information Project of the Federation of American Scientists.
- ^ Bumstead, Pamela (December 6, 1985). NUCLEAR WINTER: THE ANTHROPOLOGY OF HUMAN SURVIVAL (PDF). 84th Annual Meeting of the American Anthropological Association. Washington, D.C.: American Anthropological Association.
- ^ Limardo, Jessica. "First FEMA Incident Workforce Academy class graduates" Archived February 13, 2014, at archive.today. BioPrepWatch. February 13, 2014. (Retrieved February 13, 2014).
- ^ "Emergency Management Institute (EMI) – EMI Programs and Activities". Training.fema.gov. Archived from the original on April 17, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2016.
- ^ "Emergency Management". Frederick.edu. April 4, 2014. Archived from the original on February 20, 2014. Retrieved April 20, 2014.
- ^ Announcing the Creation of FEMA Corps. FEMA.gov (June 16, 2012). Retrieved August 16, 2013.
- ^ "Join AmeriCorps NCCC". September 16, 2022.
- ^ Welcome to the FEMA Corps Inaugural Class |Homeland Security. Dhs.gov (September 14, 2012). Retrieved August 16, 2013.
- ^ Segal AmeriCorps Education Award. Americorps.gov Retrieved March 2, 2023
- ^ "Sun-Sentinel Investigation: FEMA". Sun-Sentinel. Archived from the original on February 20, 2007. Retrieved April 18, 2007.
- ^ Kestin, Sally; O'Matz, Megan (October 10, 2004). "FEMA Gave $21 Million in Miami-Dade, Where Storms Were 'Like a Severe Thunderstorm'". Sun-Sentinel. Archived from the original on June 25, 2008. Retrieved April 18, 2007.
- ^ Kestin, Sally (June 8, 2005). "Homestead Women Sentenced to Probation for Cheating FEMA". Sun-Sentinel. Archived from the original on August 17, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2007.
- ^ Kestin, Sally (August 10, 2005). "FEMA Paid for at Least 203 Funerals Not Related to 2004 Hurricanes". Sun-Sentinel. Archived from the original on June 28, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2007.
- ^ "Q. 16, Short EAF (Part 1) 100 Year Flood Plain - NYS Dept. of Environmental Conservation". www.dec.ny.gov. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ^ Flavelle, Christopher (September 24, 2021). "The Cost of Insuring Expensive Waterfront Homes Is About to Skyrocket". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ^ "FEMA's flood insurance system, prices changing". newscentermaine.com. November 10, 2021. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ^ "How FEMA’s New Flood Insurance Rules Affect Nebraska, Iowa." n.d. Www.msn.com. Accessed November 18, 2021.
- ^ "Executive Summary, Select Bipartisan Committee to Investigate the Preparation for and Response to Hurricane Katrina" Archived February 11, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. February 15, 2006. U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved June 11, 2007.
- ^ a b "FEMA, Select Bipartisan Committee to Investigate the Preparation for and Response to Hurricane Katrina" Archived March 2, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. February 15, 2006. U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved June 11, 2007.
- ^ Duval, Stanwood R. Jr.; United States District Court; Eastern District of Louisiana (December 12, 2005). ""Order of December 12, 2005" (Rec. Doc. No. 63)" (PDF). USCourts.gov. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 7, 2007. Retrieved April 18, 2007.
"Beatrice B. Mcwaters, et al. v. Federal Emergency Management Section 'K' (3)" (No. 05-5488)
- ^ Duval, Stanwood R. Jr.; United States District Court; Eastern District of Louisiana. ""Modified Order of January 12, 2006" (Ref. Doc. No. 74)" (PDF). USCourts.gov. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 15, 2007. Retrieved April 18, 2007.
"Beatrice B. Mcwaters, et al. v. Federal Emergency Management Section 'K' (3)" (No. 05-5488)
- ^ "FEMA To Melt Ice Stored Since Katrina" . CBS News.
- ^ FEMA Gives Away $85 Million of Supplies for Katrina Victims". CNN.
- ^ "FEMA Replies to Unjustified Claims Regarding FEMA's Response To Early Snowstorm In Western New York". Federal Emergency Management Agency. Archived January 28, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Ark. Pols Blast FEMA for Tornado Response". USA Today.
- ^ "FEMA Stages Press Conference: Staff Pose As Journalists And Ask 'Softball' Questions". ThinkProgress.org. Archived from the original on May 22, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2016.
- ^ Ripley, Amanda (October 28, 2007). "Why FEMA Fakes It with the Press". Time.
- ^ a b Vick, Karl (October 9, 2017). "The Island and the Storm: Puerto Rico was wrecked by Hurricane Maria, then ignored by the mainland". Nation. TIME Magazine. Vol. 190, no. 14. pp. 26–31. ISSN 0040-781X. EBSCOhost 125386172.
- ^ "Are Hurricane Maria Survivors Getting 'Skittle Meals' From The Government?". Snopes.com. October 16, 2017. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
- ^ Walsh, Deirdre (September 26, 2017). "Ryan says Puerto Rico will get aid, calls situation 'a humanitarian crisis'". Cnn.com. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
- ^ a b c Achenbach, Joel; Hernández, Arelis R. (October 9, 2017). "FEMA administrator: Puerto Rico's politics, lack of unity, hindering hurricane response". Retrieved December 16, 2017 – via www.WashingtonPost.com.
- ^ "Port of PONCE (PR PSE) details – Departures, Expected Arrivals and Port Calls – AIS Marine Traffic". MarineTraffic.com. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- ^ Jacobs, Jennifer; Flavelle, Christopher (February 13, 2019). "FEMA Chief Brock Long Leaving Agency He Led Through Deadly Storms". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on October 17, 2019. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
Homeland Security Secretary Kirstjen Nielsen said that Long would have to reimburse the government for the cost of the vehicles and staff involved in the trips, many of which were between Washington and his home in North Carolina. The report puts that cost at $151,000.
- ^ Reid, Paula (April 8, 2019). "DHS Secretary Kirstjen Nielsen speaks for first time since resignation announcement". CBS News. Archived from the original on April 17, 2020.
- ^ a b "Historic Hurricane Harvey's Recap". Weather.com. September 2, 2017. Retrieved December 2, 2017.
- ^ "Texas Hurricane Harvey (DR-4332) – FEMA.gov". Fema.gov. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- ^ Willingham, AJ (October 10, 2017). "A look at four storms from one brutal hurricane season". Cnn.com. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- ^ "Hurricane Season 2017 – OCHA". UNOCHA.org. September 20, 2017. Archived from the original on December 15, 2017. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- ^ Levey, Noam (April 7, 2020). "Hospitals say feds are seizing masks and other coronavirus supplies without a word". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on May 4, 2020. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ Pereira, Alyssa (April 24, 2020). "Breed says SF's PPE orders have been diverted to France and 'confiscated' by FEMA". SFGate. Archived from the original on April 26, 2020. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ Stout, Matt; McGrane, Victoria (March 27, 2020). "In state's intense chase for protective equipment, coronavirus isn't the only rival — the feds are, too". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on April 18, 2020. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ Asiamah, Nancy (April 3, 2020). "3 million masks ordered by Massachusetts were seized at Port of NY in March". WWLP 22 News. Boston, Massachusetts. Archived from the original on April 12, 2020. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ Shapiro, Ariel. "Maryland Gov. Hogan Takes Extraordinary Steps To Keep Feds From Confiscating COVID Tests". Forbes. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- ^ Czachor, Emily (April 30, 2020). "National Guard protecting Maryland's coronavirus tests in undisclosed location so federal government can't seize them". Newsweek. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- ^ "Governor Larry Hogan - Official Website for the Governor of Maryland". Governor of Maryland. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- ^ Wingerter, Justin (April 8, 2020). "Feds sending 100 ventilators to Colorado, Trump says". The Denver Post. Archived from the original on April 22, 2020. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
FEMA bought 500 ventilators out from under state, governor said last week
- ^ Morfitt, Karen (May 1, 2020). "'It's A Global Free For All': Gov. Polis Says He's Making Coronavirus Supply Purchases In Secret". CBS4 Denver. Denver, Colorado. Archived from the original on May 3, 2020. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
Last month the governor made claims that FEMA swooped in to obtain ventilators he thought were coming to Colorado. He says now they're careful to keep all purchases under wraps.
- ^ a b Papenfuss, Mary (April 25, 2020). "FEMA Reportedly Took The 5 Million Masks Ordered For Veterans To Send To Stockpile". Huffington Post. Archived from the original on May 5, 2020. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
FEMA instructed vendors with protective equipment ordered by the Veterans Administration to send the shipments instead to the stockpile.
- ^ a b Settle, Allen K. (January 1985). "Financing Disaster Mitigation, Preparedness, Response, and Recovery". Public Administration Review. 45 (Special Issue: Emergency Management: A Challenge for Public Administration): 101–106. doi:10.2307/3135004. JSTOR 3135004.
- ^ a b Settle, Allen K. (1985). "Financing Disaster Mitigation, Preparedness, Response, and Recovery". Public Administration Review. 45: 101–106. doi:10.2307/3135004. ISSN 0033-3352. JSTOR 3135004.
Further reading
[edit]- Garrett, Thomas A.; Sobel, Russell S. (July 2003). "The Political Economy of FEMA Disaster Payments". Economic Inquiry. 41 (3): 496–509. doi:10.1093/ei/cbg023. ISSN 0095-2583. EBSCOhost 10360377.
- Sobel, Russell S., Christopher J. Coyne, and Peter T. Leeson. "The political economy of FEMA: did reorganization matter?." Journal of Public Finance and Public Choice 25.2-3 (2007): 151-167 online Archived October 7, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Kneeland, Timothy W. Playing Politics with Natural Disaster: Hurricane Agnes, the 1972 Election, and the Origins of FEMA (Cornell University Press, 2020) online
- Kousky, Carolyn. "Facts about FEMA household disaster aid: examining the 2008 floods and tornadoes in Missouri." Weather, Climate, and Society 5.4 (2013): 332–344. online
- Lindsay, Bruce R. FEMA Disaster Housing: The Individuals and Households Program--Implementation and Potential Issues for Congress (Congressional Research Service, 2017) online.
- Murphree, Vanessa; Bryan H., Reber; Blevens, Frederick (July 2009). "Superhero, Instructor, Optimist: FEMA and the Frames of Disaster in Hurricanes Katrina and Rita". Journal of Public Relations Research. 21 (3): 273–294. doi:10.1080/10627260802640732. eISSN 1532-754X. ISSN 1062-726X. EBSCOhost 41038900.
- Sadiq, Abdul-Akeem, Kevin Tharp, and John D. Graham. "FEMA versus local governments: Influence and reliance in disaster preparedness." Natural hazards 82.1 (2016): 123–138. online
- Schneider, Saundra K. "FEMA, federalism, Hugo, and'Frisco." Publius: The Journal of Federalism 20.3 (1990): 97–116.
- "Senate panel recommends abolishing FEMA". NBC News. The Associated Press. April 26, 2006.
- Lindsay, Bruce R. (November 30, 2012). Federal Emergency Management: A Brief Introduction (PDF) (CRS Report for Congress). Congressional Research Service. R42845. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 20, 2014.
External links
[edit]- Official website

- Federal Emergency Management Agency in the Federal Register
- "FEMA Taking Shelter From the Storm". Fema.gov. Retrieved March 6, 2019. – safe room construction plans



